作为有关 Spring Security 的系列文章的继续,在本文中我们将学习“如何在 Spring Boot 3 中使用 UserDetailsService 实现 Spring Boot 中的安全性?”。经过前面的文章,我希望我们都非常熟悉安全性的基础知识,甚至 Spring Boot 应用程序中的安全性基础知识。 Spring Boot 3 发布后,我们将在这里实现“使用 Spring Boot 3 的 Spring Security UserDetailsService”。
在本文中,我们将创建一个用户注册表单并将用户及其角色保存在数据库中。然后,根据用户角色,我们将借助预定义的 UserDetailsService 检查身份验证和授权功能。
您对整篇文章有何期望?
Spring Security 上下文中的 UserDetailsService 概念是什么?
实施 UserDetailsService 有什么好处?
如何使用 Spring Boot 3 实现 Spring Security UserDetailsService?
如何在基于 Spring 的应用程序中实现基于角色的安全性?
此外,如何以及在哪里使用注释:@EnableWebSecurity,@Configuration,@Bean,@GetMapping,@Autowired,@Data,@Entity,@Table,@Id,@GenerateValue,@Column,@ElementCollection,@CollectionTable, @JoinColumn,@Service
如何使用 Spring MVC 和 Thymeleaf 开发用户注册应用程序?
如何测试启用安全的应用程序?
如何在没有 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的情况下使用 UserDetailsService 在 Spring Boot 中实现安全性?
示例中使用的软件/技术
有时某些版本与其他版本冲突。因此,列出经过测试可以相互协作的组合。下面是经过测试的软件组合,用于使用 Spring Boot 3 开发 Spring Security UserDetailsService。它也使实现完美无缺。
JDK 17 or later
Maven 3.8.1
IDE – STS 4.7.1
Jars Used
下面是这些示例中 maven 使用 pom.xml 自动下载的主要 jar 的列表。如果您在执行中遇到任何问题,它们可能有助于交叉验证。
spring-boot-3.0.0.jar
spring-boot-starter-3.0.0.jar
spring-boot-starter-security-3.0.0.jar
spring-core-6.0.2.jar
spring-security-core-6.0.0.jar
thymeleaf-spring6-3.1.0.RELEASE.jar
UserDetailsService 是做什么的?使用它有什么好处?
UserDetailsService 是 Spring 框架在 org.springframework.security.core.userdetails 包下提供的预定义接口。为了使用 UserDetailsService,我们的实现类实现了这个接口并重写了它的 loadUserByUsername(String username) 方法。该方法的返回类型是 UserDetails,它又是一个接口。预定义的 User 类(org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User)是 UserDetails 接口的实现。此外,我们在 loadUserByUsername(String username) 方法中传递用户名,它返回我们预定义的 User 对象(org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User)。
事实上,我们只向 UserDetailsService 提供用户名和一些小配置。因此,我们将所有基于角色的内置安全功能作为框架的一部分实现。因此,当我们使用 UserDetailsService 接口时,我们在实现安全性方面节省了很多精力。
如何将 UserDetailsService 安全性合并到我们的应用程序中?
首先,您必须有一个 Spring Boot Web 应用程序,其中您将有一个表单,即一种用户注册表单。作为 Spring MVC 结构的一部分,您将拥有一个 UserService 实现类。假设它是 UserServiceImpl.java。要记住的第二件事是,您必须将 User 对象转换为预定义的 Spring User 对象。此外,请按照以下步骤在您的应用程序中实现 UserDetailsService。
1) 你的用户服务类‘UserServiceImpl.java’应该实现接口 UserDetailsService.java(由 Spring 提供)
2) 同样重要的是,重写 UserServiceImpl 类中 UserDetailsService 接口的 loadUserByUsername(String username) 方法。
3) 作为实施的一部分,
(A) 借助 UserRepository 中的用户名/电子邮件获取您的用户对象。 (B) 将你的 User 对象相应地转换为 Spring 预定义的 User 对象(org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User)。 (C) 返回 Spring 定义的 User 对象,它是 UserDetails的实现。
下面的代码代表了 UserDetailsService 的实现。但是,您将在下面的部分中看到完整的代码。
UserServiceImpl.java
import java.util.Optional;import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.model.User;import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.repo.UserRepository;import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.service.IUserService;
@Servicepublic class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService, UserDetailsService{
@Autowired private UserRepository userRepo;
@Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override public Integer saveUser(User user) { String passwd= user.getPassword(); String encodedPasswod = passwordEncoder.encode(passwd); user.setPassword(encodedPasswod); user = userRepo.save(user); return user.getId(); }
@Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String email) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
Optional<User> opt = userRepo.findUserByEmail(email);
if(opt.isEmpty()){ throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User with email: " + email +" not found !"); } else { User user = opt.get(); return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User( user.getEmail(), user.getPassword(), user.getRoles() .stream() .map(role-> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role)) .collect(Collectors.toSet()) ); }
}
}我们如何在基于 Spring 的应用程序中实现基于角色的安全性?
通常,在基于 Spring 的应用程序中,我们通过创建一个 java 类并在其上应用 @EnableWebSecurity 和 @Configuration 来实现基于角色的访问。 @EnableWebSecurity 在应用程序中启用 Spring Security 功能,而 @Configuration 表示该类是一个配置类。例如,下面的代码演示了基于角色的安全性的实现。
SecurityConfig.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher;
@EnableWebSecurity@Configurationpublic class SecurityConfig {
@Autowired private UserDetailsService uds;
@Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder;
@Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/home","/register","/saveUser").permitAll() .antMatchers("/welcome").authenticated() .antMatchers("/admin").hasAuthority("Admin") .antMatchers("/mgr").hasAuthority("Manager") .antMatchers("/emp").hasAuthority("Employee") .antMatchers("/hr").hasAuthority("HR") .antMatchers("/common").hasAnyAuthority("Employeee,Manager,Admin") .anyRequest().authenticated()
.and() .formLogin() .defaultSuccessUrl("/welcome",true)
.and() .logout() .logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout"))
.and() .exceptionHandling() .accessDeniedPage("/accessDenied")
.and() .authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
return http.build();
}
@Bean public AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() { DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider(); authenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(uds); authenticationProvider.setPasswordEncoder(encoder); return authenticationProvider; }}使用 Spring Boot 3 的 Spring Security UserDetailsService 示例
为了简化使用 Spring Boot 3 的 Spring Security UserDetailsService 的实现,让我们考虑一个用例。
Use case Details 用例详细信息
让我们假设一个小型组织的内部门户。在组织中,我们的员工扮演着各种角色,例如管理员、人力资源、经理,当然还有员工。此外,门户还具有基于角色的页面访问权限。此外,某些页面应该可供所有角色访问,例如注册和公共信息页面,而其他页面则应仅限于各自的角色。
不用说,该组织将有一个用户注册页面,即使没有登录,所有用户也必须可以访问该页面。现在让我们创建一个标准用户注册流程,如下所示。

步骤#1:在 STS中创建一个 Spring Boot Starter 项目
创建入门项目时,选择“Spring Security”、“Thymeleaf”、“Spring Web”、“Spring Data JPA”、“MySQL Driver”、“Lombok”和“Spring Boot DevTools”作为入门项目依赖项。即使您不知道如何创建 Spring Boot 入门项目,也请访问“如何在 Spring boot 中创建入门项目?”的内部链接。另外,如果您想了解有关 Lombok 的更多信息,请访问 Lombok 上的内部链接。
步骤#2:更新 application.properties 文件中的数据库属性
更新 application.properties 以连接到 MySQL 数据库。请注意,我们还可以省略 driver-class-name,因为 Spring Boot 会自动从数据库 URL 中找到它,如下所示。不过,建议保留。
#-------------------- server properties ---------------server.port=8080
#--------------------- DB Connection ------------------#AutoLoading of driver class since JDBC 4#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverspring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testBootSecurityspring.datasource.username=rootspring.datasource.password=devs
#--------------------JPA-ORM Properties-----------------spring.jpa.show-sql=truespring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update#spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernet.dialect.MySQL8Dialect步骤#3:创建用户实体和存储库类
现在创建 User.java 和 UserRepositoty.java 如下。请注意,从 Spring Boot 3.0.0 和 Spring Security 6.0 开始,所有以“javax”开头的导入语句都将替换为“jakarta”,如下面的代码所示。例如:“javax.persistence.Entity;”应替换为“jakarta.persistence.Entity;”。
同样重要的是,User.java 有一个 List 类型的变量“roles”。它将在数据库中创建一个单独的表,其中包含两列 user_id 和 user_role。此外,@ElementCollection(fetch= FetchType.EAGER)表示在获取 User 对象的同时,也同时获取角色。另一方面,UserRepository 扩展了“JpaRepository”以利用内置数据库操作。
User.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.model;
import java.util.List;
import jakarta.persistence.CollectionTable;import jakarta.persistence.Column;import jakarta.persistence.ElementCollection;import jakarta.persistence.Entity;import jakarta.persistence.FetchType;import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;import jakarta.persistence.Id;import jakarta.persistence.JoinColumn;import jakarta.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Data;
@Data@Entity@Table(name="users")public class User {
@Id @GeneratedValue @Column(name="user_id") private Integer id;
@Column(name="user_name") private String name;
@Column(name="user_passwd") private String password;
@Column(name="user_email") private String email;
@ElementCollection(fetch= FetchType.EAGER) @CollectionTable( name="roles", joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name="user_id") ) @Column(name="user_role") private List<String> roles;
}UserRepository.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.repo;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.model.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
Optional<User> findUserByEmail(String email);}步骤#4:创建 AppConfig 类来实例化 BCryptPasswordEncoder
由于 BCryptPasswordEncoder 是一个预定义的类,因此我们需要在 AppConfig.java 中提供它的实例化代码作为配置类。此外,需要 BCryptPasswordEncoder 在其他类中对我们的密码值进行编码。
AppConfig.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@Configurationpublic class AppConfig {
@Bean public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); }}步骤#5:创建服务接口和服务实现类
相应地创建服务接口和服务 Impl 类作为 IUserService.java 和 UserServiceImpl.java,如下所示。事实上,UserServiceImpl.java 中 loadUserByUsername(String email) 方法的实现是整个 UserDetailsService 中最重要的部分。
IUserService.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.service;
import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.model.User;
public interface IUserService {
public Integer saveUser(User user);}UserServiceImpl.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.service.impl;
import java.util.Optional;import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.model.User;import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.repo.UserRepository;import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.service.IUserService;
@Servicepublic class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService, UserDetailsService{
@Autowired private UserRepository userRepo;
@Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override public Integer saveUser(User user) { String passwd= user.getPassword(); String encodedPasswod = passwordEncoder.encode(passwd); user.setPassword(encodedPasswod); user = userRepo.save(user); return user.getId(); }
@Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String email) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
Optional<User> opt = userRepo.findUserByEmail(email);
if(opt.isEmpty()) throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User with email: " +email +" not found !"); else { User user = opt.get(); return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User( user.getEmail(), user.getPassword(), user.getRoles() .stream() .map(role-> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role)) .collect(Collectors.toSet()) ); }
}}步骤#6:创建一个 UserController 类
随后,为用户编写一个控制器类“UserController.java”,它将控制用户注册页面。
UserController.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.model.User;import com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.service.IUserService;
@Controllerpublic class UserController {
@Autowired private IUserService userService;
// Go to Registration Page @GetMapping("/register") public String register() { return "registerUser"; }
// Read Form data to save into DB @PostMapping("/saveUser") public String saveUser( @ModelAttribute User user, Model model ) { Integer id = userService.saveUser(user); String message = "User '"+id+"' saved successfully !"; model.addAttribute("msg", message); return "registerUser"; }}步骤#7:编写一个控制器类来浏览页面
除了 UserController,再编写一个控制器类并将其命名为“HomeController.java”。该类将负责浏览不同的页面。
HomeController.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controllerpublic class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/home") public String getHomePage() { return "homePage"; }
@GetMapping("/welcome") public String getWelcomePage() { return "welcomePage"; }
@GetMapping("/admin") public String getAdminPage() { return "adminPage"; }
@GetMapping("/emp") public String getEmployeePage() { return "empPage"; }
@GetMapping("/mgr") public String getManagerPage() { return "mgrPage"; }
@GetMapping("/hr") public String getHrPage() { return "hrPage"; }
@GetMapping("/common") public String getCommonPage() { return "commonPage"; }
@GetMapping("/accessDenied") public String getAccessDeniedPage() { return "accessDeniedPage"; }}步骤#8:编写 UI 页面(Thymeleaf)
以下是 UI 页面的 .html 文件。将这些页面相应地放入“src/main/resources/templates”文件夹中。
registerUser.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>User Registration</title> </head> <body> <h3>User Registration</h3> <form action="saveUser" method="post"> <pre>Name : <input type="text" name="name"/>
Email: <input type="text" name="email"/>
Password: <input type="password" name="password"/>
Role(s): <input type="checkbox" name="roles" value="Admin"/>Admin <input type="checkbox" name="roles" value="Manager"/>Manager <input type="checkbox" name="roles" value="HR"/>HR <input type="checkbox" name="roles" value="Employee"/>Employee<input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}"/> <input type="submit" value="Register"/>
</pre> </form> <div th:text="${msg}"></div> </body></html>homePage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>welcome to the Home Page</h3> This page is accessible to ALL. </body></html>welcomePage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>Welcome Page after successful Login</h3> <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>adminPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>Admin Page</h3> Welcome to Admin page.!!! <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>empPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>Employee Page</h3> <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>mgrPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>Manager Page</h3> <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>hrPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>HR Page</h3> <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>commonPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>You are not allowed to access this page. Please go to Welcome Page</h3> <a th:href="@{/welcome}">Welcome</a> <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>accessDeniedPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1" /> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>You are not allowed to access this page. Please go to Welcome Page</h3> <a th:href="@{/welcome}">Welcome</a> <a th:href="@{/logout}">LOGOUT</a> </body></html>步骤#9:编写 SecurityConfig 类而不使用 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
最后,编写另一个重要的类 SecurityConfig.java。在 Spring Security 5.7.0-M2 之前,此类应该扩展预定义的类 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.java 并相应地实现两个 configure() 方法。但从 Spring Security 5.7.0-M2 开始,WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 已被弃用。此外,从 Spring Boot 3.0.0 和 Spring Security 6.0 开始,WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 已从 Spring Security API 中完全删除。
因此,所需的实现自 Spring 3.0.0 起就适用,如下面的代码片段所示。
SecurityConfig.java
package com.dev.springboot.security.UserDetailsService.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher;
@EnableWebSecurity@Configurationpublic class SecurityConfig {
@Autowired private UserDetailsService uds;
@Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder;
@Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests() .requestMatchers("/home","/register","/saveUser").permitAll() .requestMatchers("/welcome").authenticated() .requestMatchers("/admin").hasAuthority("Admin") .requestMatchers("/mgr").hasAuthority("Manager") .requestMatchers("/emp").hasAuthority("Employee") .requestMatchers("/hr").hasAuthority("HR") .requestMatchers("/common").hasAnyAuthority("Employeee", "Manager", "Admin") .anyRequest().authenticated()
.and() .formLogin() .defaultSuccessUrl("/welcome",true)
.and() .logout() .logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout"))
.and() .exceptionHandling() .accessDeniedPage("/accessDenied")
.and() .authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
return http.build();
}
@Bean public AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() { DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider(); authenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(uds); authenticationProvider.setPasswordEncoder(encoder); return authenticationProvider; }}从上面的 SecurityConfig 实现中可以明显看出,旧版本中的一些方法也被删除了。例如:
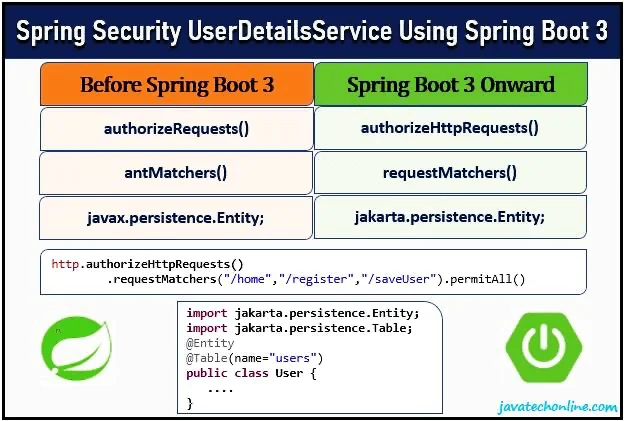
authorizeRequests() -> authorizeHttpRequests()
antMatchers() -> requestMatchers()
regexMatchers() -> RegexRequestMatchers()
最后,我们完成了编码部分。
如何测试启用安全性的应用程序?
虽然“测试”这个词对于开发人员来说看起来很容易,但它同样重要,因为它提供了我们整体实现的结果。在测试应用程序时,您应该将 SecurityConfig 类的 configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法保留在您面前,然后按照以下步骤操作:
启动应用程序:右键单击项目,然后选择“Run As”>>“Spring Boot App”。
输入注册页面 URL http://localhost:8080/register,然后检查是否每个人都可以访问,甚至不需要登录应用程序。
输入必填字段值并相应地单击“注册”按钮完成注册过程。
现在输入您在注册时选择的角色特定的任何 URL。假设您输入 URL http://localhost:8080/admin,那么它应该将您重定向到内置的登录页面。
输入凭据并登录到应用程序。它会将您重定向到默认的成功 URL,即欢迎页面。
现在再次输入 URL http://localhost:8080/admin,这次您将能够访问管理页面。
对其他角色也重复上述步骤。
此外,如上所述,将 SecurityConfig.java 代码保留在您面前,并随后测试每个场景。
如何使用 Spring Boot 3 将以前的实现迁移到 Spring Security UserDetailsService?
以下是一些分步指南,您可以按照这些指南从旧版本实现迁移到使用 Spring Boot 3 的 Spring Security UserDetailsService。
- 根据推荐 Spring 官方文档,如果使用较低版本实现,请先将实现升级到 Spring Boot 2.7.0。我们可以通过更新 pom.xml 中的 Spring Boot 版本来做到这一点,如下所示。
<parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.7.0</version><relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --></parent>更新后,保存 pom.xml 并让 Maven 下载新的依赖项。
对于此示例,您将发现 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 已被弃用。提供新的实现,而不使用 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter。您可以使用本文中的 SecurityConfig.java 实现。如果还有其他错误,也请修复它们。
下一步,按照 Spring Boot 官方文档的建议在项目中配置 JDK 17 环境。
在 pom.xml 中将 Spring Boot 版本更新为“3.0.0”,保存文件并让 maven 下载新的依赖项。
修复编译错误,如下图:
(A) I 在 SecurityConfig.java 中:
将 authorizeRequests() 替换为 authorizeHttpRequests()
将 antMatchers() 替换为 requestMatchers()
将 regexMatchers() 替换为 RegexRequestMatchers()
(B) 在实体类中:
将所有出现的“javax”替换为“jakarta”。例如:“javax.persistence.Entity;”应替换为“jakarta.persistence.Entity;”。
故障排除
将 Spring Boot 版本升级到 3.0.0 时,您可能会遇到以下错误:
[ERROR] Some problems were encountered while processing the POMs:[ERROR] 'dependencies.dependency.version' for org.thymeleaf.extras:thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5:jar is missing.为了解决此错误,请更新 Thymeleaf 的版本,如下所示。
<dependency><groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId><artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId><version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version></dependency>更新完成后,maven 会自动下载合适的依赖项。
概括
在完成“使用 Spring Boot 3 的 Spring Security UserDetailsService”的所有理论和示例部分之后,最后,我们应该能够在 Spring Boot 项目中实现基于角色的 Web 安全性。当然,在本文中我们介绍了实现安全功能的第三种方法。同样,我们将在接下来的文章中讨论更多安全方法。未来若有任何变化,我们将进行相应更新。
如果您想了解 Spring Boot 3.0 中的新增功能,请访问我们关于“Spring Boot 3 中的新功能”的单独文章。另外,欢迎在评论区提出你的意见。
原文链接:https://javatechonline.com/spring-security-userdetailsservice-using-spring-boot-3/