Git使用
部署Git 服务
创建git仓库
git-server上的操作:
[root@localhost ~]# yum install git git-core gitweb -y
[root@localhost ~]# useradd git
[root@localhost ~]# passwd git
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /git-root/
[root@localhost ~]# cd /git-root/
[root@localhost git-root]# git init --bare shell.git
Initialized empty Git repository in /git-root/shell.git/
[root@localhost git-root]# chown -R git:git shell.git
注意: git init 和 git init –bare 的区别:
- 使用–bare选项时,不再生成 .git 目录,而是只生成 .git 目录下面的版本历史记录文件,这些版本历史记录文件也不再存放在 .git 目录下面,而是直接存放在版本库的根目录下面。
- 用"git init"初始化的版本库用户也可以在该目录下执行所有 git 方面的操作。但别的用户在将更新 push 上来的时候容易出现冲突。 使用”git init –bare”方法创建一个所谓的裸仓库,之所以叫裸仓库是因为这个仓库只保存git历史提交的版本信息,而不允许用户在上面进行各种git操作,如果你硬要操作的话,只会得到下面的错误(”This operation must be run in a work tree”)这个就是最好把远端仓库初始化成bare仓库的原因
git仓库测试
git-client上的操作:
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id git@192.168.1.178
[root@localhost shell]# git config --global user.email "you@example.com"
[root@localhost shell]# git config --global user.name "Your Name"
[root@localhost ~]# git clone git@192.168.1.178://git-root/shell.git
[root@localhost ~]# ls
rh shell
[root@localhost ~]# cd shell/
[root@localhost shell]# vim test.sh
[root@localhost shell]# git add test.sh
[root@localhost shell]# git commit -m 'first commit'
[master (root-commit) 33c5fbf] first commit
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 test1.sh
[root@localhost shell]# git push origin master
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 230 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To git@192.168.1.178://git-root/shell.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Git 客户端安装使用
Git 安装配置
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install curl-devel expat-devel gettext-devel openssl-devel zlib-devel
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install git git-all git-core
[root@localhost ~]# git --version
git version 2.18.4
Git 配置
Git 提供了一个叫做 git config 的工具,专门用来配置或读取相应的工作环境变量。
这些环境变量,决定了 Git 在各个环节的具体工作方式和行为。这些变量可以存放在以下三个不同的地方:
/etc/gitconfig文件:系统中对所有用户都普遍适用的配置。若使用git config时用--system选项,读写的就是这个文件。~/.gitconfig文件:用户目录下的配置文件只适用于该用户。若使用git config时用--global选项,读写的就是这个文件。- 当前项目的 Git 目录中的配置文件(也就是工作目录中的
.git/config文件):这里的配置仅仅针对当前项目有效。每一个级别的配置都会覆盖上层的相同配置,所以.git/config里的配置会覆盖/etc/gitconfig中的同名变量。
1、Git 用户信息
配置个人的用户名称和电子邮件地址:
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global user.name "test"
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global user.email test@qq.com
如果用了 –global 选项,那么更改的配置文件就是位于你用户主目录下的那个,以后你所有的项目都会默认使用这里配置的用户信息。
如果要在某个特定的项目中使用其他名字或者电邮,只要去掉 –global 选项重新配置即可,新的设定保存在当前项目的 .git/config 文件里。
2、文本编辑器
设置Git默认使用的文本编辑器, 一般可能会是 Vi 或者 Vim。如果你有其他偏好,比如 Emacs 的话,可以重新设置
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global core.editor emacs
3、差异分析工具
还有一个比较常用的是,在解决合并冲突时使用哪种差异分析工具。比如要改用 vimdiff 的话:
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global merge.tool vimdiff
Git 可以理解 kdiff3,tkdiff,meld,xxdiff,emerge,vimdiff,gvimdiff,ecmerge,和 opendiff 等合并工具的输出信息。
当然,你也可以指定使用自己开发的工具
4、查看配置信息
要检查已有的配置信息,可以使用 git config –list 命令:
[root@localhost ~]# git config --list
http.postbuffer=2M
user.name=runoob
user.email=test@runoob.com
有时候会看到重复的变量名,那就说明它们来自不同的配置文件(比如 /etc/gitconfig 和 ~/.gitconfig),不过最终 Git 实际采用的是最后一个。
这些配置我们也可以在 ~/.gitconfig 或 /etc/gitconfig 看到,如下所示:
[root@localhost ~]# vim ~/.gitconfig
显示内容如下所示:
[http]
postBuffer = 2M
[user]
name = git
email = test@localhost.com
也可以直接查阅某个环境变量的设定,只要把特定的名字跟在后面即可,像这样:
[root@localhost ~]# git config user.name
git
Git 使用
1、ssh 链接
客户机上产生公钥上传到gitlab的SSH-Keys里,git clone下载和git push上传都没问题,这种方式很安全
2、http 链接(两种方式实现)
1、修改代码里的 .git/config 文件添加登录用户名密码
[root@localhost ~]# cd .git
[root@localhost ~]# cat config
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = true
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
[remote "origin"]
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
url = http://username:password@localhost@172.17.0.39:sauser/ansible.git
[branch "master"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/master
2、 执行命令设置登录用户和密码
# cd到根目录,执行
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global credential.helper store # 执行之后会在.gitconfig文件中多添加以下选项
[credential]
helper = store
# cd到项目目录,执行git pull命令,会提示输入账号密码。输完这一次以后就不再需要,并且会在根目录生成一个.git-credentials文件
[root@localhost ~]# git pull
Username for 'http://172.17.0.39:sauser/ansible.git':
xxxx@xxxx.com Password for 'https://xxxx@xxxx.com@172.17.0.39:sauser/ansible.git':
[root@localhost ~]# cat .git-credentials
https://Username:Password@localhost.oschina.net
# 之后pull/push代码都不再需要输入账号密码了
3、设置身份验证
**注意:**设定本机用户名,绑定邮箱,让远程服务器知道机器的身份
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global user.name "user_name"
[root@localhost ~]# git config --global user.email "XXXXX@XX.com"
4、本地项目与远程服务器项目之间的交互
1、如果你没有最新的代码,希望从头开始
[root@localhost ~]# git clone git@XXX.git # 这里是项目的地址(可从项目主页复制),将远程服务器的内容完全复制过来
[root@localhost ~]# cd BGBInspector_V01 # clone 之后进入该项目的文件夹
[root@localhost ~]# touch README.md # 新建readme文件
[root@localhost ~]# git add README.md # 将新的文件添加到git的暂存区
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m ‘Its note:add a readme file’ # 将暂存区的文件提交到某一个版本保存下来,并加上注释
[root@localhost ~]# git push -u origin master # 将本地的更改提交到远程服务器
2、如果你已经有一个新版代码,希望直接把本地的代码替换到远程服务器
[root@localhost ~]# cd existing_folder #进入代码存在的文件夹,或者直接在该文件夹打开
[root@localhost ~]# git init # 初始化
[root@localhost ~]# git remote add origin git@master://git-test/shell.git #添加远程项目"shell"库的地址(可从项目主页复制) ,前提是事先需要先在git远程服务器上创建相应的裸库"shell"
[root@localhost ~]# git add . #添加该文件夹中所有的文件到git的暂存区
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m ‘note’ #提交所有代码到本机的版本库
[root@localhost ~]# git push -u origin master #将本地的更改提交到远程服务器
git 中 clone过来的时候,git 不会对比本地和服务器的文件,也就不会有冲突,
建议确定完全覆盖本地的时候用 clone,不确定会不会有冲突的时候用 git pull,将远程服务器的代码download下来
git pull=git fetch+git merge
实验如下:
#本地代码内容如下: [root@node1 shell]# cat mem.sh free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $4}' echo hello echo ni hao #远程Git服务器代码内容如下: [root@node1 shell]# cat mem.sh free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $4}' echo hello echo ni hao echo ha ha #本地机器做fetch操作: [root@node1 shell]# git fetch origin master:test remote: Enumerating objects: 5, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done. From master://git-test/shell * [new branch] master -> test b522245..10f9569 master -> origin/master #fetch是把远程代码作为本地的一个其他分支下载到本地,并不更新本地分支,这里的命令是把远程的”master“分支下载到本地作为一个新的分支”test“存在 #查看本地文件并没有发生变化 [root@node1 shell]# ls mem.sh [root@node1 shell]# cat mem.sh free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $4}' echo hello echo ni hao #用diff查看本地master分支和fetch下来的test分支有什么区别: [root@node1 shell]# git diff master test diff --git a/mem.sh b/mem.sh index 7ce0803..c0c8cef 100644 --- a/mem.sh +++ b/mem.sh @@ -1,3 +1,4 @@ free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $4}' echo hello echo ni hao +echo ha ha #如果发现fetch下来的代码没什么问题,可以选择和本地分支进行合并 [root@node1 shell]# git merge Updating eb8645c..10f9569 Fast-forward mem.sh | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) [root@node1 shell]# cat mem.sh free -m | awk 'NR==2{print $4}' echo hello echo ni hao echo ha ha
5、常用的git 命令
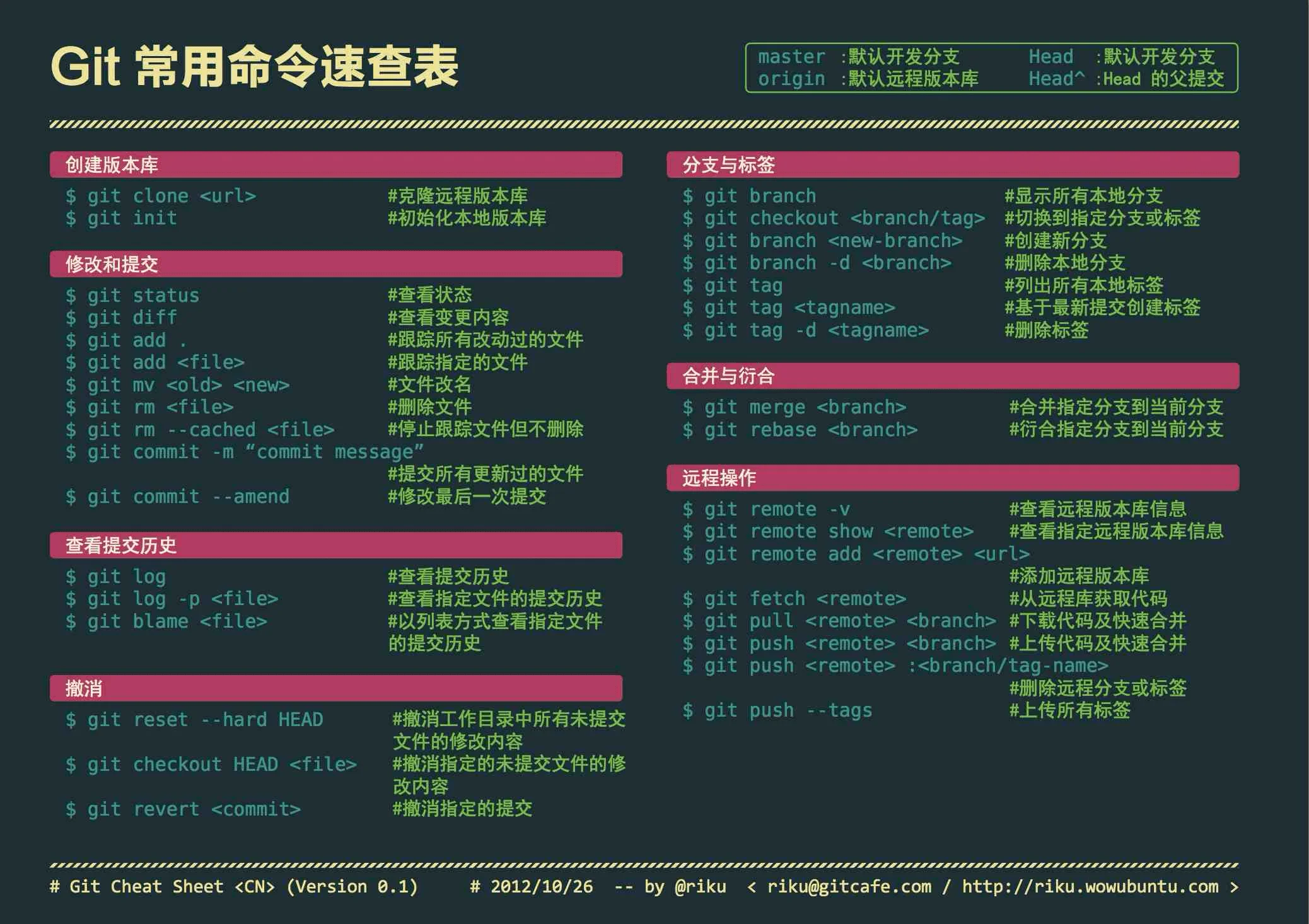
[root@localhost ~]# git init # 初始化
[root@localhost ~]# git add main.cpp # 将某一个文件添加到暂存区
[root@localhost ~]# git add . # 将文件夹下的所有的文件添加到暂存区
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m ‘note‘ # 将暂存区中的文件保存成为某一个版本
[root@localhost ~]# git log # 查看所有的版本日志
[root@localhost ~]# git status # 查看现在暂存区的状况
[root@localhost ~]# git diff # 查看现在文件与上一个提交-commit版本的区别
[root@localhost ~]# git reset --hard HEAD^ # 回到上一个版本
[root@localhost ~]# git reset --hard XXXXX # XXX为版本编号,回到某一个版本
[root@localhost ~]# git pull origin master # 从主分支pull到本地
[root@localhost ~]# git push -u origin master # 从本地push到主分支
[root@localhost ~]# git pull # pull默认主分支
[root@localhost ~]# git push # push默认主分支 ...
6、版本穿梭
1、版本回退
# 用 git log 命令查看:
# 每一个提交的版本都唯一对应一个 commit 版本号,
# 使用 git reset 命令退到上一个版本:
[root@localhost ~]# git reset --hard HEAD^
[root@localhost ~]# git reflog # 查看命令历史,以便确定要回到哪个版本
[root@localhost ~]# git reset --hard commit_id # 比如git reset --hard 3628164(不用全部输入,输入前几位即可)
2、分支管理
1、创建分支
[root@localhost ~]# git checkout -b dev #创建dev分支,然后切换到dev分支
[root@localhost ~]# git checkout #命令加上-b参数表示创建并切换,相当于以下两条命令:
[root@localhost ~]# git branch dev && git checkout dev
[root@localhost ~]# git branch #命令查看当前分支,会列出所有分支,当前分支前面会标一个*号
[root@localhost ~]# git add readme.txt git commit -m "branch test" # 在dev分支上正常提交.
2、分支切换
[root@localhost ~]# git checkout master #切换回master分支
# 查看一个readme.txt文件,刚才添加的内容不见了,因为那个提交是在dev分支上,而master分支此刻的提交点并没有变
3、合并分支
[root@localhost ~]# git merge dev #把dev分支的工作成果合并到master分支上
[root@localhost ~]# git merge #命令用于合并指定分支到当前分支。
# 合并后,再查看readme.txt的内容,就可以看到,和dev分支的最新提交是完全一样的。
注意到上面的Fast-forward信息,Git告诉我们,这次合并是“快进模式”,也就是直接把master指向dev的当前提交,所以合并速度非常快。 当然,也不是每次合并都能Fast-forward,我们后面会讲其他方式的合并。
[root@localhost ~]# git branch -d dev #删除dev分支了:
删除后,查看branch,就只剩下master分支了.
3、解决冲突
[root@localhost ~]# git checkout -b feature1 # 创建新的feature1分支
# 修改readme.txt最后一行,改为:
Creating a new branch is quick AND simple.
[root@localhost ~]# git add readme.txt # 在feature1分支上提交
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m "AND simple"
[root@localhost ~]# git checkout master #切换到master分支
Switched to branch 'master' Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 1 commit.
#Git还会自动提示我们当前master分支比远程的master分支要超前1个提交。
#在master分支上把readme.txt文件的最后一行改为:
Creating a new branch is quick & simple.
[root@localhost ~]# git add readme.txt
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m "& simple"
#现在,master分支和feature1分支各自都分别有新的提交
#这种情况下,Git无法执行“快速合并”,只能试图把各自的修改合并起来,但这种合并就可能会有冲突,我们试试看:
git merge feature1 Auto-merging readme.txt CONFLICT (content):
Merge conflict in readme.txt Automatic merge failed;
fix conflicts and then commit the result.
readme.txt文件存在冲突,必须手动解决冲突后再提交。
[root@localhost ~]# git status 可以显示冲突的文件;
#直接查看readme.txt的内容:
Git is a distributed version control system.
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
Git tracks changes of files.
<<<<<<< HEAD Creating a new branch is quick & simple. ======= Creating a new branch is quick AND simple. >>>>>>> feature1
#Git用<<<<<<<,=======,>>>>>>>标记出不同分支的内容,我们修改后保存再提交:
[root@localhost ~]# git add readme.txt
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m "conflict fixed"
[master 59bc1cb] conflict fixed
#最后,删除feature1分支:
[root@localhost ~]# git branch -d feature1
Deleted branch feature1 (was 75a857c).
Github 远程仓库
1、github.com 注册账户
2、github 上创建仓库
3、本地服务器生成 ssh 公钥
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa -C 'meteor@163.com' # 邮箱要与github上注册的相同
[root@localhost ~]# cat .ssh/id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDVThfq4brrlsPGtAknVB0TLPx+7Dd3qlxTbSIrUOsGC5Y8JuNqVTlIntZB4oNj8cSQrWvec9CKm0a8o7WwaJIiqpxurz+YpQHP2KbapftKIxsX4hPf/z+p0El1U6arQa35/xmNsq+cJLH/bDdRG+EMDhuCBmjVZOlLj/hEdeIT6s56AnnCkaWoF+sq58KCF7Tk54jRbs/YiyE4SN7FuA70r+07sA/uj0+lmuk4E190KtQUELhjX/E9stivlqiRhxnKvVUqXDywsjfM8Rtvbi4Fg9R8Wt9fpd4QwnWksYUoR5qZJFYXO4hSZrUnSMruPK14xXjDJcFDcP2eHIzKgLD1 meteor@163.com
4、 github 添加 ssh 公钥
复制以上的公钥,在 github 中添加ssh key
5、测试连接
[root@localhost ~]# yum install git
........
[root@localhost ~]# ssh -T git@localhost.com
The authenticity of host 'github.com (13.250.177.223)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:nThbg6kXUpJWGl7E1IGOCspRomTxdCARLviKw6E5SY8.
RSA key fingerprint is MD5:16:27:ac:a5:76:28:2d:36:63:1b:56:4d:eb:df:a6:48.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'github.com,13.250.177.223' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
Hi meteor! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.
[root@localhost ~]#
6、连接远程仓库(创建一个测试存储库)
# 在 github 网站新建一个仓库,命名为linux
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir linux
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir linux
[root@localhost ~]# cd linux
# git 初始化,然后做第一个基本的git操作(需要在github上创建存储库)
[root@localhost ~]# git init
[root@localhost ~]# touch README
[root@localhost ~]# git add README
[root@localhost ~]# git commit -m 'first commit'
[root@localhost ~]# git remote add origin git@localhost.com:userhub/linux.git
# 若出现origin已经存在的错误,删除origin
[root@localhost linux]# git remote rm origin
# 现在继续执行push到远端
[root@localhost linux]# git remote add origin git@localhost.com:userhub/linux.git
[root@localhost linux]# git push -u origin master
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 205 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To git@localhost.com:fakehydra/linux-.git
* [new branch] master -> master
# 分支 master 设置为跟踪来自 origin 的远程分支 master。
# 注意
# 设置存储库链接
[root@localhost ~]# git remote set-url origin git@localhost.com:userhub/linux.git
# 如果 push 失败,合并分支到 master 再 push
[root@localhost ~]# git pull --rebase origin master
