ActiveMQ源码-BrokerService和PersistenceAdapter
activemq-broker 模块 test/java 目录下有个 IDERunner 类:
public class IDERunner { private static final boolean TRANSPORT_TRACE = false;
public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception { BrokerService brokerService = new BrokerService();
// brokerService.addConnector(// "tcp://0.0.0.0:61616?trace=" + TRANSPORT_TRACE +// "&transport.wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600");
brokerService.setPersistent(false); brokerService.setUseJmx(false); brokerService.setAdvisorySupport(false);
brokerService.start(); brokerService.waitUntilStopped(); }}注释掉 brokerService 调用 addConnector 方法的三行代码,然后 debug 运行该类的 main 方法。
BrokerService
BrokerService 管理 ActiveMQ Broker 的生命周期。BrokerService 由许多传输连接器、网络连接器和一系列属性组成,这些属性可用于在延迟创建代理时对其进行配置。
BrokerService 类实现了 Service 接口。Service 接口是 ActiveMQ 组件的核心生命周期接口。如果有标准方法,最好将此接口注册到 Spring,以便它将启动/ 停止方法视为 org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean 和 org.springframework. beans.factory.DisposableBean 的方法
public interface Service { void start() throws Exception; void stop() throws Exception;}BrokerService 类没有构造方法,有一个 static 代码块:
static { try { Boolean bouncyCastleNotAdded = Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.activemq.broker.BouncyCastleNotAdded"); if (bouncyCastleNotAdded == null || bouncyCastleNotAdded == false) { ClassLoader loader = BrokerService.class.getClassLoader(); Class<?> clazz = loader.loadClass("org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider"); Provider bouncycastle = (Provider) clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); Integer bouncyCastlePosition = Integer.getInteger("org.apache.activemq.broker.BouncyCastlePosition"); int ret; if (bouncyCastlePosition != null) { ret = Security.insertProviderAt(bouncycastle, bouncyCastlePosition); } else { ret = Security.addProvider(bouncycastle); } LOG.info("Loaded the Bouncy Castle security provider at position: {}", ret); } } catch(Throwable e) { // No BouncyCastle found so we use the default Java Security Provider }
String localHostName = "localhost"; try { localHostName = InetAddressUtil.getLocalHostName(); } catch (UnknownHostException e) { LOG.error("Failed to resolve localhost"); } LOCAL_HOST_NAME = localHostName;
String version = null; try(InputStream in = BrokerService.class.getResourceAsStream("/org/apache/activemq/version.txt")) { if (in != null) { try(InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(isr)) { version = reader.readLine(); } } } catch (IOException ie) { LOG.warn("Error reading broker version", ie); } BROKER_VERSION = version;}上面代码的主要逻辑:
- 加载 Bouncy Castle security provider
- 获取当前主机的名称
- 从 /org/apache/activemq/version.txt 文件获取当前 activemq 版本
BrokerService 实现了 Service 接口,程序启动入口方法为 start 方法,停止方法为 stop 方法。
start 方法:
1、判断是否已经启动。用到了 stopped 和 started 两个变量。
//private final AtomicBoolean started = new AtomicBoolean(false);//private final AtomicBoolean stopped = new AtomicBoolean(false);if (stopped.get() || !started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {// lets just ignore redundant start() calls// as its way too easy to not be completely sure if start() has been// called or not with the gazillion of different configuration// mechanisms// throw new IllegalStateException("Already started.");return;}2、初始化变量 startException、stopping、preShutdownHooksInvoked、startDate
3、将 brokerName (默认为 localhost)保存到 MDC 上下文中的 activemq.broker 中
4、 检查内存使用限制
5、检查 systemExitOnShutdown 和 useShutdownHook 不能同时为 true
6、处理 transportConnectorURIs、networkConnectorURIs、jmsBridgeConnectors 属性,用于调用 addConnector、addNetworkConnector、addJmsConnector 方法。
7、注册 JMX
8、使用 brokerName 将 当前 BrokerService 绑定到 BrokerRegistry
9、启动持久化适配器 PersistenceAdapter,可以设置是否异步启动
10、启动 Broker,可以设置是否异步启动
11、从 MDC 删除 activemq.broker
调用链如下:
BrokerService BrokerRegistry PersistenceAdapter PListStore JobSchedulerStore Broker TransportConnector TransportServer TransportConnection Transport NetworkConnector ProxyConnector JmsConnectorBrokerRegistry
BrokerRegistry 是一个单例类,BrokerRegistry内部维护了一个 INSTANCE 实例,通过对 mutex 对象添加同步锁来确保 BrokerRegistry 类的线程安全。
private static final BrokerRegistry INSTANCE = new BrokerRegistry();
private final Object mutex = new Object(); private final Map<String, BrokerService> brokers = new HashMap<String, BrokerService>();
public static BrokerRegistry getInstance() { return INSTANCE; }查找方法:
public BrokerService lookup(String brokerName) { BrokerService result = null; synchronized (mutex) { result = brokers.get(brokerName); if (result == null && brokerName != null && brokerName.equals(BrokerService.DEFAULT_BROKER_NAME)) { result = findFirst(); if (result != null) { LOG.warn("Broker localhost not started so using {} instead", result.getBrokerName()); } } if (result == null && (brokerName==null || brokerName.isEmpty() || brokerName.equals("null"))){ result = findFirst(); } } return result;}
public BrokerService findFirst() { synchronized (mutex) { Iterator<BrokerService> iter = brokers.values().iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { return iter.next(); } return null; }}绑定和解绑方法:
public void bind(String brokerName, BrokerService broker) { synchronized (mutex) { brokers.put(brokerName, broker); mutex.notifyAll(); }}
public void unbind(String brokerName) { synchronized (mutex) { brokers.remove(brokerName); }}注意:bind 方法中调用了 mutex.notifyAll(); 方法用于唤醒其他想获取 mutex 锁的阻塞的线程。
PersistenceAdapter
为防止因系统崩溃而导致消息丢失,消息中间件一般会支持消息持久化便于服务重启后恢复原来的消息数据。
通常消息持久化的逻辑是:当生产者发送消息后,Broker 首先将消息存储到文件、内存或数据库等地方,然后再将消息发送给消费者,发送成功后将消息从存储中删除,若失败则继续尝试发送。Broker 在启动时会先检查指定位置的存储,若有发送失败的消息,则继续发送。
在 JMS 规范中对消息转发模式有两种:持久化(Persistent) 和 非持久化(Non_Persistent)。ActiveMQ 实现了 JSM 规范,即也支持这两种消息转发模式。
持久化(PERSISTENT)
对于持久化消息,被发送到消息服务器后,会被持久化存储,如果当前没有消费者,则会继续存在,只有等到消息被处理并被消费确认后,才会被消息服务器删除。
该模式保证消息在被成功消费之前不会丢失。
非持久化(NON_PERSISTENT)
JMS 实现者必须保证尽最大努力分发消息,但消息不会持久化存储。非持久化消息通常用于发送通知或不重要的实时数据。
该模式消息保证最多只传递一次,不保证消息不丢失。若看重系统性能并且即使丢失一些消息也不会影响业务正常运行,可选择非持久化消息。
PersistenceAdapter接口是一个关键组件,用于定义数据持久化的行为
startPersistenceAdapter 方法:
private void startPersistenceAdapter(boolean async) throws Exception { if (async) { new Thread("Persistence Adapter Starting Thread") { @Override public void run() { try { doStartPersistenceAdapter(); } catch (Throwable e) { setStartException(e); } finally { synchronized (persistenceAdapterStarted) { persistenceAdapterStarted.set(true); persistenceAdapterStarted.notifyAll(); } } } }.start(); } else { doStartPersistenceAdapter(); }}如果传入参数 async 为 true,则启动一个线程进行异步操作(使用 persistenceAdapterStarted 保存状态);否则为同步调用。
doStartPersistenceAdapter 方法:
1、初始化 PersistenceAdapter 对象
public synchronized PersistenceAdapter getPersistenceAdapter() throws IOException {if (persistenceAdapter == null && !hasStartException()) {persistenceAdapter = createPersistenceAdapter();configureService(persistenceAdapter);this.persistenceAdapter = registerPersistenceAdapterMBean(persistenceAdapter);}return persistenceAdapter;}createPersistenceAdapter:创建 PersistenceAdapter
- 如果开启持久化 persistent =true,则
- PersistenceAdapterFactory 不为空,则调用 PersistenceAdapterFactory.createPersistenceAdapter() 方法
- 否则,通过反射初始化 KahaDBPersistenceAdapter 对象,并设置持久化目录为
${org.apache.activemq.default.directory.prefix}/activemq-data/${brokerName}/KahaDB
- 如果没有开启持久化,则返回 MemoryPersistenceAdapter
- 如果开启持久化 persistent =true,则
configureService:配置 Service
protected void configureService(Object service) {if (service instanceof BrokerServiceAware) {BrokerServiceAware serviceAware = (BrokerServiceAware) service;serviceAware.setBrokerService(this);}}registerPersistenceAdapterMBean:注册 JMX
2、判断启动时是否删除所有消息
if (deleteAllMessagesOnStartup) {LOG.info("Deleting all messages on startup because deleteAllMessagesOnStartup configuration has been provided");deleteAllMessages();}public void deleteAllMessages() throws IOException {getPersistenceAdapter().deleteAllMessages();}3、启动 PersistenceAdapter
4、初始化 tempDataStore 即 PListStore
public synchronized PListStore getTempDataStore() {if (tempDataStore == null && !hasStartException()) {if (!isPersistent()) {return null;}try {PersistenceAdapter pa = getPersistenceAdapter();if( pa!=null && pa instanceof PListStore) {return (PListStore) pa;}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}try {String clazz = "org.apache.activemq.store.kahadb.plist.PListStoreImpl";this.tempDataStore = (PListStore) getClass().getClassLoader().loadClass(clazz).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();this.tempDataStore.setDirectory(getTmpDataDirectory());configureService(tempDataStore);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException("Kahadb class PListStoreImpl not found. Add activemq-kahadb jar or set persistent to false on BrokerService.", e);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}return tempDataStore;}5、启动 PListStore
6、初始化 JobSchedulerStore
7、启动 JobSchedulerStore
PersistenceAdapter 接口的定义:
public interface PersistenceAdapter extends Service { Set<ActiveMQDestination> getDestinations();
// 创建 MessageStore MessageStore createQueueMessageStore(ActiveMQQueue destination) throws IOException; TopicMessageStore createTopicMessageStore(ActiveMQTopic destination) throws IOException; JobSchedulerStore createJobSchedulerStore() throws IOException, UnsupportedOperationException; TransactionStore createTransactionStore() throws IOException;
// 删除 MessageStore void removeQueueMessageStore(ActiveMQQueue destination); void removeTopicMessageStore(ActiveMQTopic destination);
// 事务 void beginTransaction(ConnectionContext context) throws IOException; void commitTransaction(ConnectionContext context) throws IOException; void rollbackTransaction(ConnectionContext context) throws IOException;
// 删除消息 void deleteAllMessages() throws IOException;
void setUsageManager(SystemUsage usageManager); void setBrokerName(String brokerName); void setDirectory(File dir); File getDirectory(); void checkpoint(boolean cleanup) throws IOException;
long size(); long getLastProducerSequenceId(ProducerId id) throws IOException; long getLastMessageBrokerSequenceId() throws IOException; void allowIOResumption();}PersistenceAdapter 实现类:
- MemoryPersistenceAdapter:基于内存的 PersistenceAdapter
- KahaDBPersistenceAdapter:基于 KahaDB 的 PersistenceAdapter
- MultiKahaDBPersistenceAdapter:基于多个 KahaDB 的 PersistenceAdapter
- JDBCPersistenceAdapter:基于 JDBC 数据库的 PersistenceAdapter
- TempKahaDBStore:临时的 KahaDB PersistenceAdapter
MemoryPersistenceAdapter
基于内存的 PersistenceAdapter 最简单,先了解 MemoryPersistenceAdapter 的实现。
JMS 规范中定义了两种模型:Queue 和 Topic。对应的,在 MemoryPersistenceAdapter 里面使用 Map 来保存 Queue 和 Topic。
MemoryTransactionStore transactionStore;
ConcurrentMap<ActiveMQDestination, TopicMessageStore> topics = new ConcurrentHashMap<ActiveMQDestination, TopicMessageStore>();ConcurrentMap<ActiveMQDestination, MessageStore> queues = new ConcurrentHashMap<ActiveMQDestination, MessageStore>();
private boolean useExternalMessageReferences;protected BrokerService brokerService;topics 和 queues 的 key 是 ActiveMQDestination,值是 MessageStore。一个 destination 对应一个 Queue 或者 Topic,并对应一个 MessageStore。
public interface MessageStore extends Service { void addMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message) throws IOException; void addMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message, boolean canOptimizeHint) throws IOException;
ListenableFuture<Object> asyncAddQueueMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message) throws IOException; ListenableFuture<Object> asyncAddQueueMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message, boolean canOptimizeHint) throws IOException; ListenableFuture<Object> asyncAddTopicMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message) throws IOException; ListenableFuture<Object> asyncAddTopicMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message, boolean canOptimizeHint) throws IOException;
Message getMessage(MessageId identity) throws IOException;
void removeMessage(ConnectionContext context, MessageAck ack) throws IOException; void removeAsyncMessage(ConnectionContext context, MessageAck ack) throws IOException; void removeAllMessages(ConnectionContext context) throws IOException;
void recover(MessageRecoveryListener container) throws Exception;
ActiveMQDestination getDestination(); void setMemoryUsage(MemoryUsage memoryUsage); int getMessageCount() throws IOException; long getMessageSize() throws IOException; MessageStoreStatistics getMessageStoreStatistics();
void resetBatching();
void recoverNextMessages(int maxReturned, MessageRecoveryListener listener) throws Exception; void recoverNextMessages(int offset, int maxReturned, MessageRecoveryListener listener) throws Exception;
void dispose(ConnectionContext context); void setBatch(MessageId messageId) throws Exception; boolean isEmpty() throws Exception;
public void setPrioritizedMessages(boolean prioritizedMessages); public boolean isPrioritizedMessages();
void updateMessage(Message message) throws IOException; void registerIndexListener(IndexListener indexListener);}在内存模式下,MessageStore 的实现有 MemoryMessageStore 和 MemoryTopicMessageStore。
AbstractMessageStore 是一个抽象类,实现了 MessageStore 接口:
abstract public class AbstractMessageStore implements MessageStore { public static final ListenableFuture<Object> FUTURE; protected final ActiveMQDestination destination; protected boolean prioritizedMessages; protected IndexListener indexListener; protected final MessageStoreStatistics messageStoreStatistics = new MessageStoreStatistics();
public AbstractMessageStore(ActiveMQDestination destination) { this.destination = destination; } //...}通过构造方法,可以看到创建一个 MessageStore ,需要一个 ActiveMQDestination。AbstractMessageStore 内部还有一个 IndexListener 和 MessageStoreStatistics。IndexListener 是一个回调,作用是在消息索引更新时执行一些有序的工作。MessageStoreStatistics 用于记录和管理消息存储统计信息。
ActiveMQ 中统计相关的接口设计如下:
public interface Stats { public Statistic getStatistic(String statisticName); public String[] getStatisticNames(); public Statistic[] getStatistics();}
public interface Statistic { public String getName(); public String getUnit(); public String getDescription(); public long getStartTime(); public long getLastSampleTime();}
// Statistic // StatisticImpl // CountStatisticImpl // SizeStatisticImpl
// Stats // StatsImpl // MessageStoreStatistics创建 Queue 和 Topic 时,需要事务支持,ActiveMQ 定义了 TransactionStore 接口:
public interface TransactionStore extends Service { void prepare(TransactionId txid) throws IOException;
void commit(TransactionId txid, boolean wasPrepared, Runnable preCommit,Runnable postCommit) throws IOException;
void rollback(TransactionId txid) throws IOException;
void recover(TransactionRecoveryListener listener) throws IOException;}TransactionStore 是在 MessageStore 基础上添加事务的功能。MemoryPersistenceAdapter 类创建 MessageStore 时,会使用 TransactionStore 代理 MessageStore,例如 createQueueMessageStore 方法:
@Overridepublic MessageStore createQueueMessageStore(ActiveMQQueue destination) throws IOException { MessageStore rc = queues.get(destination); if (rc == null) { rc = new MemoryMessageStore(destination); if (transactionStore != null) { rc = transactionStore.proxy(rc); } queues.put(destination, rc); } return rc;}在内存模式下,TransactionStore 的实现有 MemoryTransactionStore。
MemoryPersistenceAdapter 创建 TransactionStore:
@Overridepublic TransactionStore createTransactionStore() throws IOException { if (transactionStore == null) { transactionStore = new MemoryTransactionStore(this, brokerService); } return transactionStore;}MemoryPersistenceAdapter 删除消息:
@Overridepublic void deleteAllMessages() throws IOException { for (Iterator<TopicMessageStore> iter = topics.values().iterator(); iter.hasNext();) { MemoryMessageStore store = asMemoryMessageStore(iter.next()); if (store != null) { store.delete(); } } for (Iterator<MessageStore> iter = queues.values().iterator(); iter.hasNext();) { MemoryMessageStore store = asMemoryMessageStore(iter.next()); if (store != null) { store.delete(); } }
if (transactionStore != null) { transactionStore.delete(); }}MemoryMessageStore
内存消息存储主要是存储所有的消息在 JVM 内存中,当重启JVM之后会丢失持久化的消息。
使用 MemoryMessageStore 条件是设置 persistent 为 false。
设置方法,第一种是设置 activemq.xml 文件:
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" persistent="false" brokerName="brokerName" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}">第二种方法是通过 BrokerService 对象进行设置:
BrokerService brokerService = new BrokerService(); brokerService.setPersistent(false); brokerService.setUseJmx(true); brokerService.start();addMessage 方法:使用了两次 synchronized
@Overridepublic synchronized void addMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message) throws IOException { synchronized (messageTable) { messageTable.put(message.getMessageId(), message); incMessageStoreStatistics(getMessageStoreStatistics(), message); message.incrementReferenceCount(); message.getMessageId().setFutureOrSequenceLong(sequenceId++); if (indexListener != null) { indexListener.onAdd(new IndexListener.MessageContext(context, message, null)); } }}removeMessage 方法:
public void removeMessage(MessageId msgId) throws IOException { synchronized (messageTable) { Message removed = messageTable.remove(msgId); if (removed != null) { removed.decrementReferenceCount(); decMessageStoreStatistics(getMessageStoreStatistics(), removed); } if ((lastBatchId != null && lastBatchId.equals(msgId)) || messageTable.isEmpty()) { lastBatchId = null; } }}recover 方法:
@Overridepublic void recover(MessageRecoveryListener listener) throws Exception { // the message table is a synchronizedMap - so just have to synchronize here synchronized (messageTable) { for (Message message : messageTable.values()) { listener.recoverMessage(message); } }}removeAllMessages 方法:
@Overridepublic void removeAllMessages(ConnectionContext context) throws IOException { synchronized (messageTable) { messageTable.clear(); getMessageStoreStatistics().reset(); }}MemoryTopicMessageStore
MemoryTopicMessageStore是一个用于存储主题(Topic)消息的内存消息存储实现。
字段:
private Map<SubscriptionKey, SubscriptionInfo> subscriberDatabase;private Map<SubscriptionKey, MemoryTopicSub> topicSubMap;private final Map<MessageId, Message> originalMessageTable;- topicSubMap:保存主题订阅
添加订阅:
@Overridepublic synchronized void addSubscription(SubscriptionInfo info, boolean retroactive) throws IOException { SubscriptionKey key = new SubscriptionKey(info); MemoryTopicSub sub = new MemoryTopicSub(key); topicSubMap.put(key, sub); if (retroactive) { for (Map.Entry<MessageId, Message> entry : messageTable.entrySet()) { sub.addMessage(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } } subscriberDatabase.put(key, info);}addMessage 方法:
@Overridepublic synchronized void addMessage(ConnectionContext context, Message message) throws IOException { super.addMessage(context, message); for (MemoryTopicSub sub : topicSubMap.values()) { sub.addMessage(message.getMessageId(), message); }}MemoryTransactionStore
protected ConcurrentMap<Object, Tx> inflightTransactions = new ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Tx>();protected Map<TransactionId, Tx> preparedTransactions = Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap<TransactionId, Tx>());protected final PersistenceAdapter persistenceAdapter;protected final BrokerService brokerService;
private boolean doingRecover;MemoryTransactionStore 类的 proxy 方法会对 MessageStore、TopicMessageStore 进行代理,例如代理 addMessage、removeMessage 方法,转而使用 MemoryTransactionStore 自己的 addMessage、removeMessage方法(如果开启了事务,则创建 Tx 对象,保存到 List<AddMessageCommand> messages 或者 List<RemoveMessageCommand> acks)。
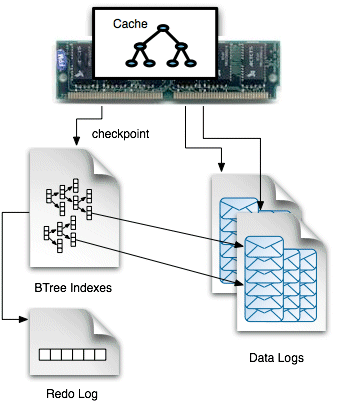
KahaDBPersistenceAdapter
KahaDB 是 ActiveMQ 框架的基于文件的持久性数据库。它位于使用它的消息代理的本地,已针对快速持久性进行了优化。它是自ActiveMQ Classic 5.4以来的默认存储机制。与其前身AMQ 消息存储相比,KahaDB 使用更少的文件描述符并提供更快的恢复速度。